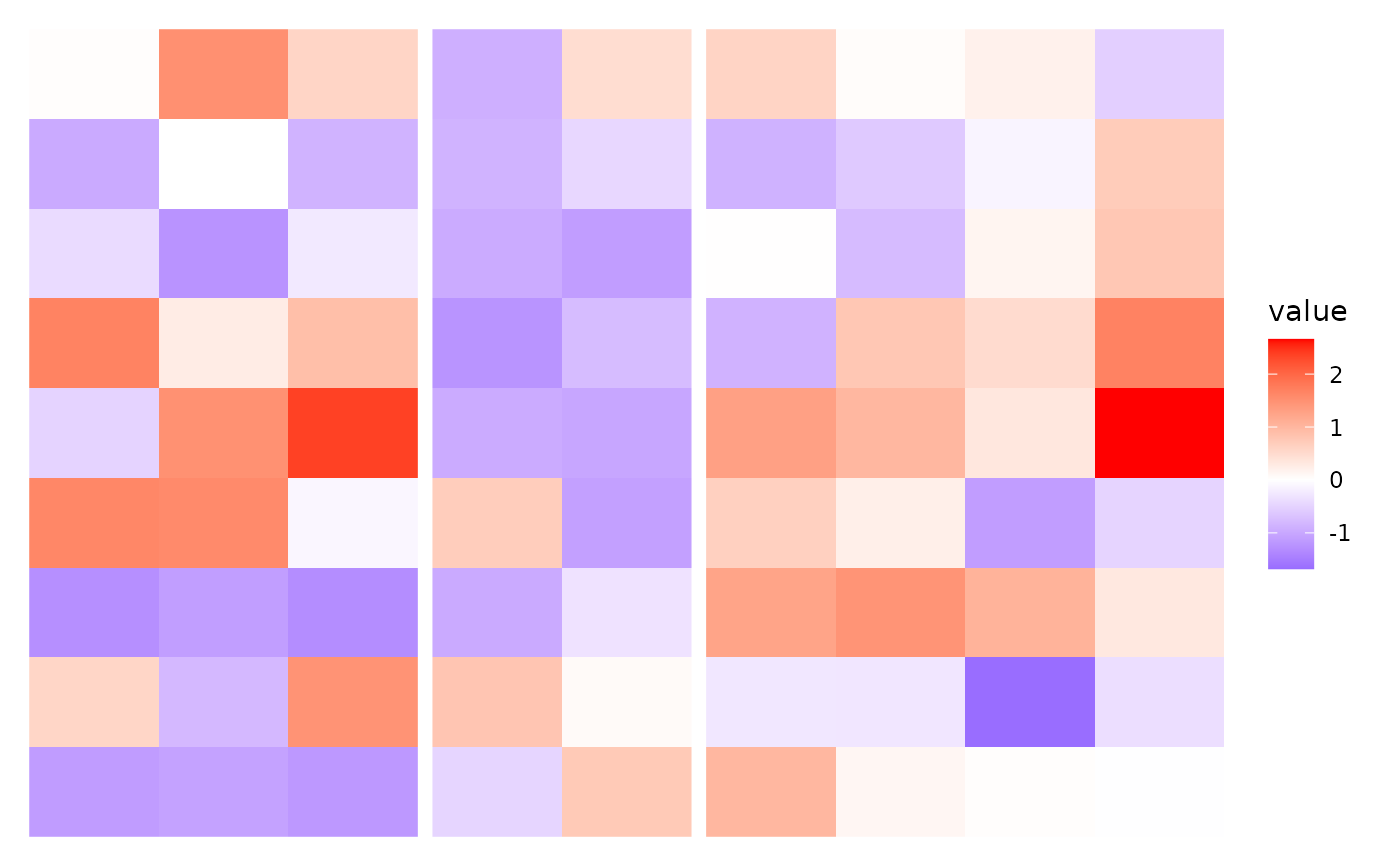
Aligns and groups observations based on k-means clustering, enabling observation splits by cluster groups.
Arguments
- ...
Arguments passed on to
stats::kmeansiter.maxthe maximum number of iterations allowed.
nstartif
centersis a number, how many random sets should be chosen?algorithmcharacter: may be abbreviated. Note that
"Lloyd"and"Forgy"are alternative names for one algorithm.tracelogical or integer number, currently only used in the default method (
"Hartigan-Wong"): if positive (or true), tracing information on the progress of the algorithm is produced. Higher values may produce more tracing information.
- data
A numeric matrix to be used by k-means. By default, it will inherit from the layout matrix.
- active
A
active()object that defines the context settings when added to a layout.