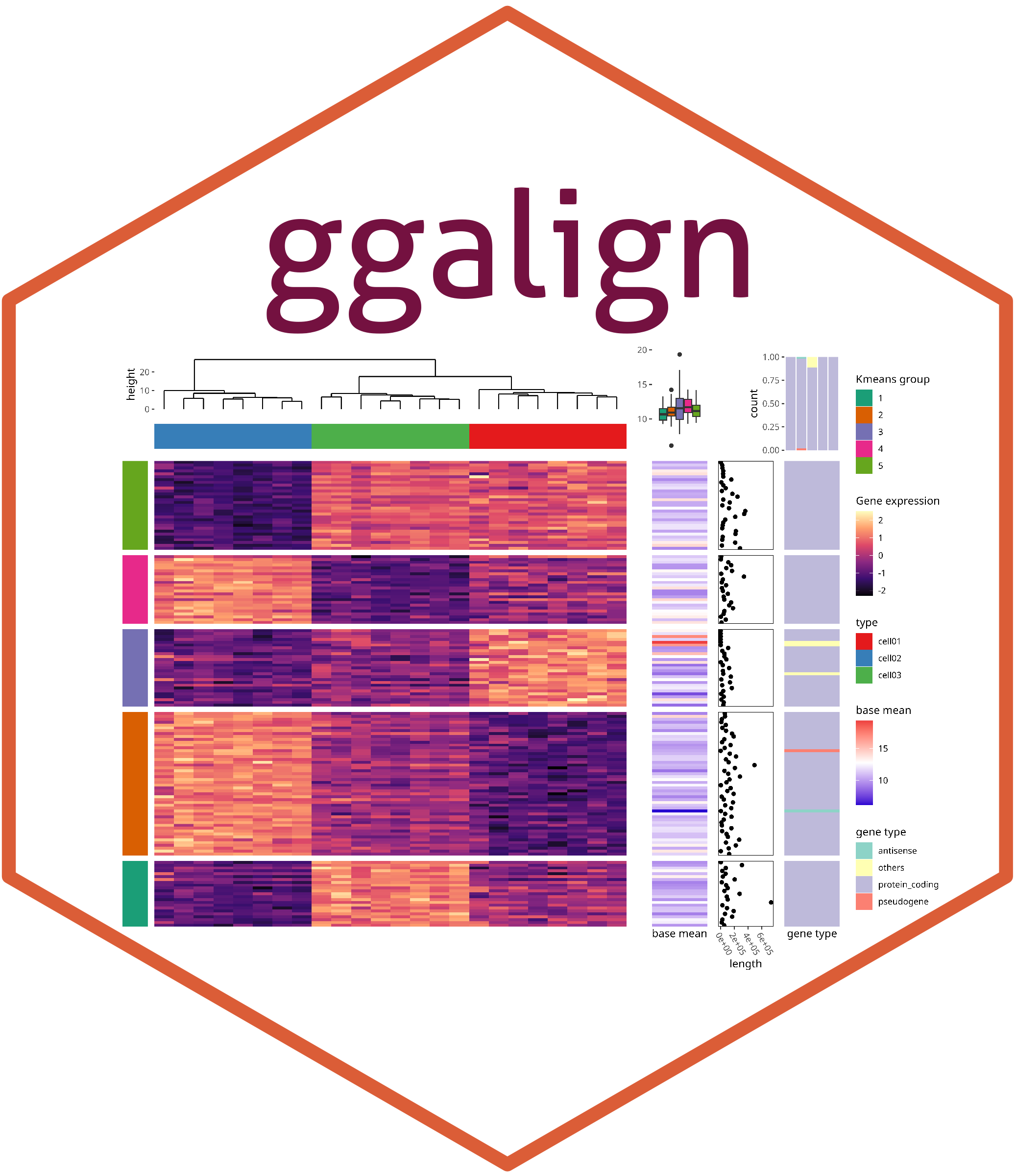
Usage
align_order(
weights = rowMeans,
...,
reverse = FALSE,
strict = TRUE,
data = NULL,
active = NULL
)Arguments
- weights
A summary function which accepts a data and returns the weights for each observations. Alternatively, you can provide an ordering index as either an integer or a character. Since characters have been designated as character indices, if you wish to specify a function name as a string, you must enclose it with
I().- ...
<dyn-dots> Additional arguments passed to function provided in
weightsargument.- reverse
A boolean value. Should the sort order be in reverse?
- strict
A boolean value indicates whether the order should be strict. If previous groups has been established, and strict is
FALSE, this will reorder the observations in each group.- data
A
matrix,data frame, or atomic vector used as the input for theweightsfunction. Alternatively, you can specify afunction(including purrr-like lambda syntax) that will be applied to the layout matrix, transforming it as necessary for weight calculations. By default, it will inherit from the layout matrix.- active
A
active()object that defines the context settings when added to a layout.