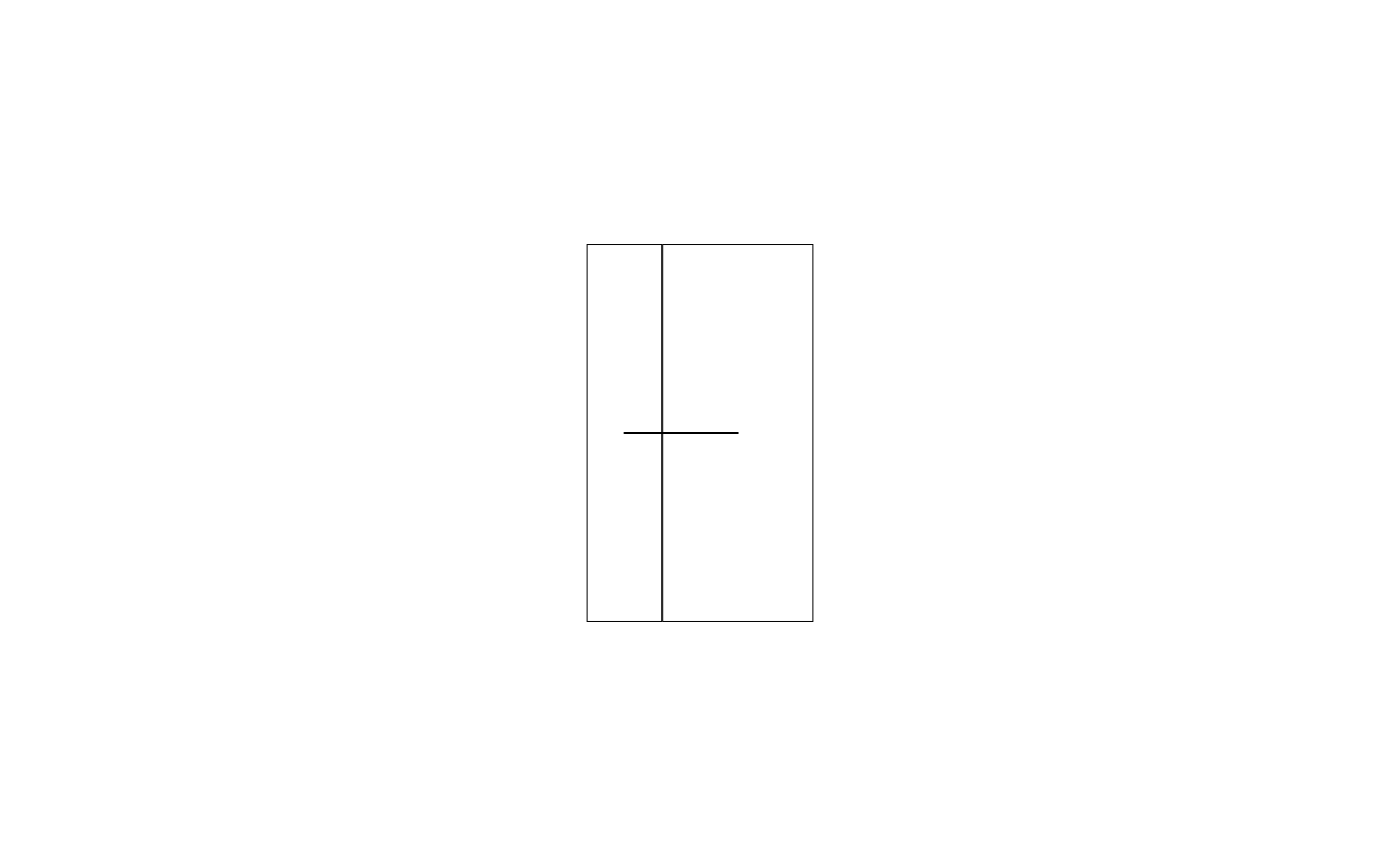
This function initializes a communication channel to share location signals
across different viewports. It returns a channelSenderGrob object, which
can transmit multiple signals using its $signal method (see the "Signal"
section below for details). When drawn, all collected signals are passed to
the make_content function to generate the final grob.
Signal
A channelSenderGrob can emit multiple location signals using the $signal
method. This method accepts the following arguments:
x: X-coordinate.y: Y-coordinate.default.units: The default units forxandy.tag: A character string used to identify the location.name: A name for the returned grob.vp: Aviewportfor the returned grob.
The $signal method returns a channelSignalGrob.
Examples
# we create a new channel, we will emit two singals
# here: we just add a line between the two signals
channel <- channelGrob(function(locations) {
# you can also use `tag` to identify the locations
loc1 <- .subset2(locations, 1L)
loc2 <- .subset2(locations, 2L)
grid::segmentsGrob(loc1$x, loc1$y, loc2$x, loc2$y)
})
gt <- gtable::gtable(unit(1:2, c("cm")), unit(5, "cm"))
gt <- gtable::gtable_add_grob(
gt,
list(
grid::rectGrob(gp = gpar(color = "black", fill = NA)),
channel$signal(0.5, 0.5, "npc")
),
t = 1, l = 1, name = c("rect1", "signal1")
)
gt <- gtable::gtable_add_grob(
gt,
list(
grid::rectGrob(gp = gpar(color = "red", fill = NA)),
channel$signal(0.5, 0.5, "npc")
),
t = 1, l = 2, name = c("rect2", "signal2")
)
grid::grid.newpage()
grid::grid.draw(gt)