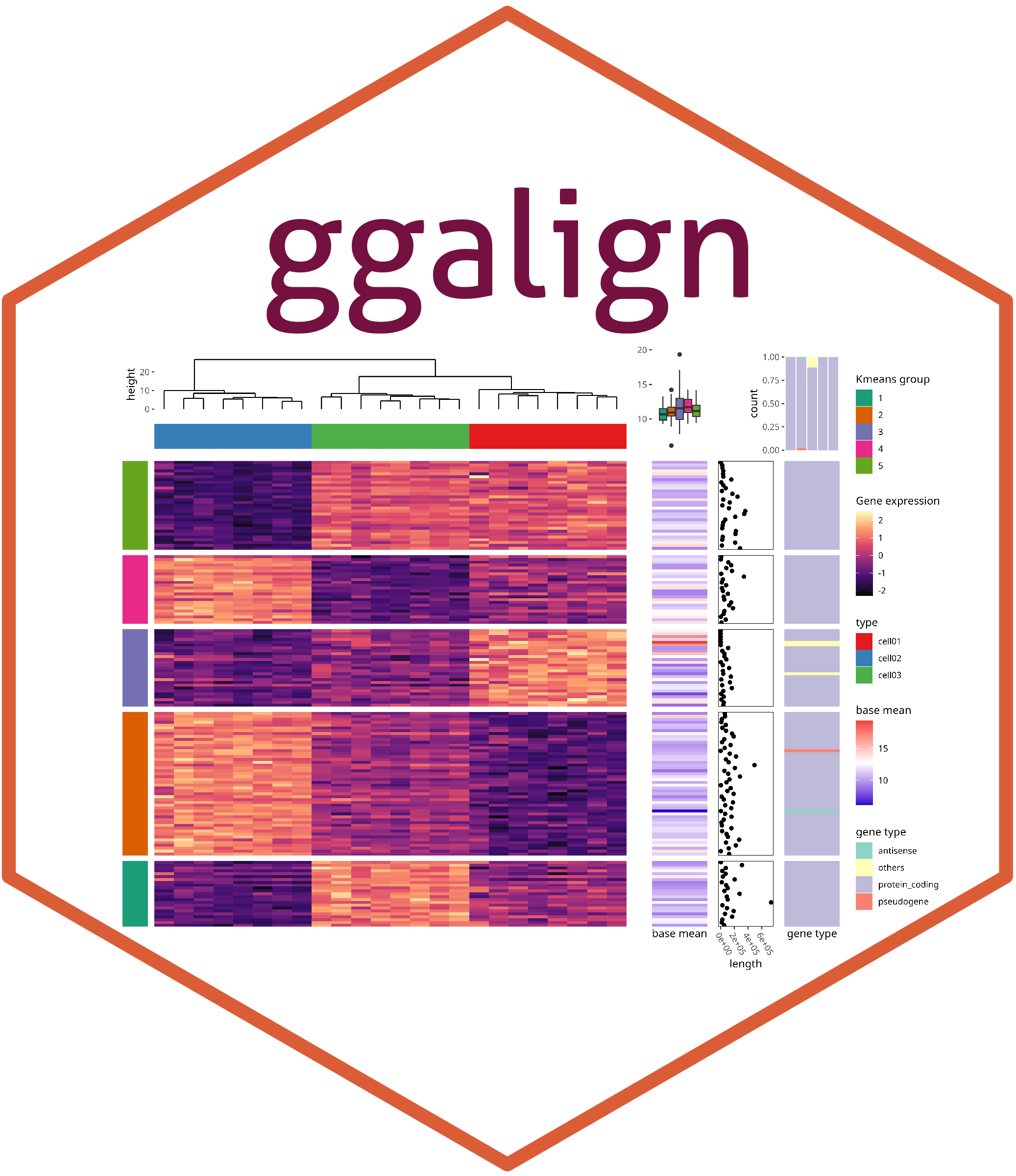
ggheatmap is an alias of layout_heatmap.
Usage
layout_heatmap(
data,
mapping = aes(),
...,
filling = TRUE,
set_context = TRUE,
order = NULL,
name = NULL
)
ggheatmap(
data,
mapping = aes(),
...,
filling = TRUE,
set_context = TRUE,
order = NULL,
name = NULL
)Arguments
- data
A numeric or character vector, a data frame, and any other data which can be converted into a matrix. Simple vector will be converted into a one column matrix.
- mapping
Default list of aesthetic mappings to use for plot. If
NULL, will usingaes(.data$.x, .data$.y).- ...
Additional arguments passed to geom_tile. Only used when
filling = TRUE.- filling
A boolean value indicates whether to fill the heatmap. If you want to custom the filling style, you can set to
FALSE.- set_context
A single boolean value indicates whether to set the active context to current plot. If
TRUE, all subsequent ggplot elements will be added into this plot.- order
An single integer for the layout order.
- name
A string of the plot name. Used to switch the active context in
hmanno()orstack_active().
ggplot2 specification
The data input in ggheatmap will be converted into the long formated data
frame when drawing. The default mapping will use aes(.data$.x, .data$.y),
you can use mapping argument to control it. The data in the underlying
ggplot object contains following columns:
.xpaneland.ypanel: the column and row panel.xand.y: thexandycoordinates.row_namesand.column_names: A factor of the row and column names of the original matrix (only applicable when names exist)..row_indexand.column_index: the row and column index of the original matrix.value: the actual matrix value.