Plot options control the actions of plots within the layout. These options can be applied either globally to all plots in the layout or individually to specific plots.
- To apply a plot option to a single plot, use the
+operator. - To set a plot option at the layout level (affecting all plots), use
the
-operator.
Plot options inherit properties from parent layout options hierarchically.
The package currently provides three plot options, each prefixed with
plot_:
-
plot_theme: Sets the default theme for the plot. -
plot_data: Transforms the plot data. Many functions in this package require a specific data format to align observations,plot_data()helps reformat data frames as needed. -
plot_align: Defines alignment specifications for plots within the layout.
set.seed(123)
small_mat <- matrix(rnorm(81), nrow = 9)
rownames(small_mat) <- paste0("row", seq_len(nrow(small_mat)))
colnames(small_mat) <- paste0("column", seq_len(ncol(small_mat)))
plot_theme
The plot_theme() function extends theme()
to set a default theme for plots, allowing you to input
theme() elements directly or modify the theme elements.
To set a plot option for a single plot, simply use the +
operator:
ggheatmap(small_mat) +
# change the default theme of the heatmap body
plot_theme(plot.background = element_rect(fill = "red"))
#> → heatmap built with `geom_tile()`
Using a theme() Object in plot_theme().
ggheatmap(small_mat, filling = FALSE) +
geom_tile(aes(fill = value), width = 0.9, height = 0.9) +
# change the default theme of the heatmap body
plot_theme(theme_bw(), plot.background = element_rect(fill = "red"))
Note that plot_theme() serves as the default theme and
will always be overridden by any theme() settings applied
directly to the plot. The default theme (plot_theme()) is
applied first, followed by any specific theme() settings,
even if theme() is added before
plot_theme().
ggheatmap(small_mat) +
# change the plot theme of the heatmap body
theme(plot.background = element_rect(fill = "blue")) +
# change the default theme of the heatmap body
plot_theme(plot.background = element_rect(fill = "red"))
#> → heatmap built with `geom_tile()`
By using the - operator with plot options, we apply the
option directly to the active layout.
ggheatmap(small_mat) +
# Change the active layout to the top annotation
anno_top() +
# add a dendrogram to the top annotation
align_dendro() +
# add a bar plot to the top annotation
ggalign(aes(.names, value, fill = factor(.names)), data = rowSums) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity") -
# Change the default theme of the top annotation
# All plots in the top annotation will inherit this default theme
plot_theme(plot.background = element_rect(fill = "red"))
#> → heatmap built with `geom_tile()`
Unlike individual ggplot2 elements added to each plot, layout-level
options set by - operator are inherited by all plots in the
layout when rendered. Any plot-specific options will override these
layout-level options, regardless of the order in which they are
added.
ggheatmap(small_mat) +
# Change the active layout to the top annotation
anno_top() +
# add a dendrogram to the top annotation
align_dendro() +
# change the plot_theme for the dendrogram plot
plot_theme(plot.background = element_rect(fill = "blue")) +
# add a bar plot to the top annotation
ggalign(aes(.names, value, fill = factor(.names)), data = rowSums) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity") -
# Change the default theme of the top annotation
# All plots in the top annotation will inherit this default theme
# But the plot-specific options will override these
plot_theme(plot.background = element_rect(fill = "red"))
#> → heatmap built with `geom_tile()`
plot_data
align_gg()/ggalign() requires the specific
data format for its operations. If you need to transform or filter data
for individual geoms, you can use the data
argument within each geom. However, if you have multiple
geoms and want a consistent transformation applied across
all, you can utilize the plot_data() function. This allows
you to transform the default data for the entire plot.
The plot_data() accepts a function that takes a data
frame as input and returns a modified data frame. By default,
plot_data() will attempt to inherit from the parent layout
if the data is inherited from it. However, there is one exception:
align_dendro() will not inherit plot_data()
transformations by default.
set.seed(1234L)
ggheatmap(small_mat) +
anno_top() +
align_kmeans(3L) +
# we add a bar plot
ggalign() +
# we subest the plot data
plot_data(~ subset(.x, .panel == 1L)) +
geom_bar(aes(y = value, fill = .row_names), stat = "identity")
#> → heatmap built with `geom_tile()`
plot_align
The plot_align() function defines the align
Specifications for plots.
guides
By default, ggheatmap() will collect all guide legends
on the side from which they originate.
heatmap_collect_all_guides <- ggheatmap(small_mat, width = 2, height = 2L) +
scale_fill_viridis_c(name = "I'm from heatmap body") +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = -60, hjust = 0)) +
anno_top() +
align_dendro(aes(color = branch), k = 3L) +
scale_color_brewer(
name = "I'm from top annotation", palette = "Dark2",
guide = guide_legend(position = "right")
) +
anno_left() +
align_dendro(aes(color = branch), k = 3L) +
scale_color_brewer(
name = "I'm from left annotation", palette = "Dark2",
guide = guide_legend(position = "top", direction = "vertical")
) +
anno_bottom() +
align_dendro(aes(color = branch), k = 3L) +
scale_color_brewer(
name = "I'm from bottom annotation", palette = "Dark2",
guide = guide_legend(position = "left")
) +
anno_right() +
align_dendro(aes(color = branch), k = 3L) +
scale_color_brewer(
name = "I'm from right annotation", palette = "Dark2",
guide = guide_legend(position = "bottom", direction = "vertical")
) &
theme(plot.margin = margin())
heatmap_collect_all_guides
#> → heatmap built with `geom_tile()`
Use the guides argument control which side of guide
legends should be gathered. In the following example, we’ll collect the
guide legends only on the top and bottom
sides:
heatmap_collect_all_guides +
# reset the active context to the heatmap layout
quad_active() -
# we set global `guides` argument for the heatmap layout
# we only collect guides in the top and bottom side
plot_align(guides = "tb")
#> → heatmap built with `geom_tile()`
You can also apply the plot_align() function directly to
specific plots:
heatmap_collect_all_guides +
# reset the active context to the heatmap layout
quad_active() -
# we set global `guides` argument for the heatmap layout
# we only collect guides in the top and bottom side
plot_align(guides = "tb") +
# `+` apply it to the current active plot
# for the heatmap body, we collect guide in the right side
plot_align(guides = "r")
#> → heatmap built with `geom_tile()`
The guide legends within the annotation stack are first collected by
the stack_layout() itself and then passed to the overall
heatmap layout for further integration. By default, it inherits the
guides arguments from the heatmap layout. See following
example:
heatmap_collect_all_guides +
# reset the active context to the heatmap layout
quad_active() -
# we set global `guides` argument for the heatmap layout
# we only collect guides in the top and bottom side
plot_align(guides = "tb") +
# we ensure the active context is in the bottom annotation
# By default, it inherits "guides" argument from the heamtap layout, which
# means it'll collect "guides" in the top and bottom side
anno_bottom() +
# for the dendrogram in the bottom annotation, we collect guide in the left side
plot_align(guides = "l")
#> → heatmap built with `geom_tile()`
Here, the guide legend is collected by the bottom annotation but will
not be collected by the heatmap layout since the heatmap layout only
gathers guides from the top and bottom. In
this way, the guide legends of the annotation stack will be put around
the annotation stack layout.
To override this guide collection behavior for the heatmap
annotation, you can use the free_guides argument of the
quad_anno()/anno_*() function. This differs
from the guides argument in plot_align(),
which controls the behavior for the plots in the layout. The
free_guides argument specifies which guide legends from the
annotation stack layout should be collected by the heatmap layout.
heatmap_collect_all_guides +
# reset the active context to the heatmap layout
quad_active() -
# we set global `guides` argument for the heatmap layout
# we only collect guides in the top and bottom side
plot_align(guides = "tb") +
# we also collect guides in the left side for the bottom annotation stack
# layout in the heatmap layout
anno_bottom(free_guides = "l") +
# for the dendrogram in the bottom annotation, we collect guide in the left side
plot_align(guides = "l")
#> → heatmap built with `geom_tile()`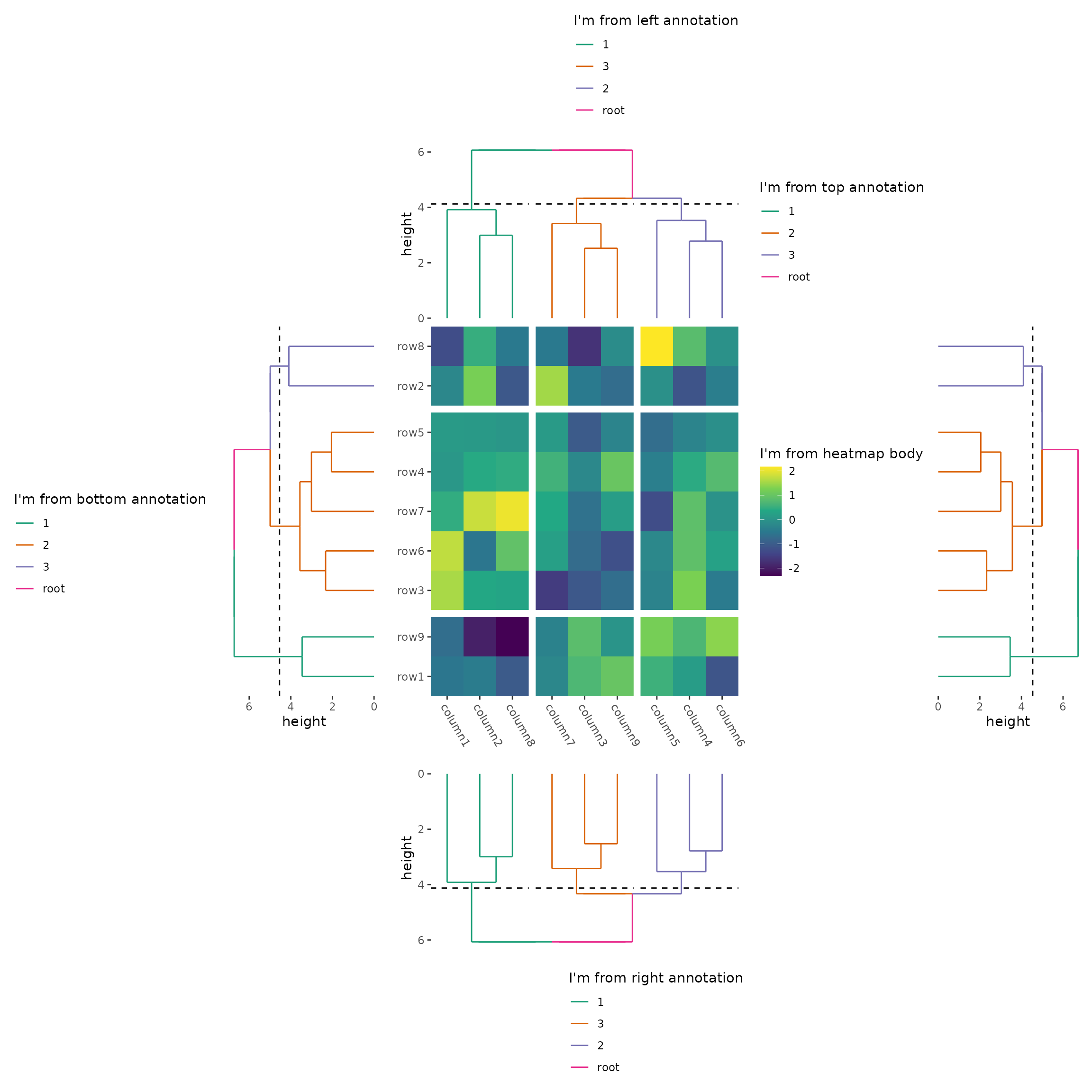
Note: The heatmap layout will only collect guide legends from the annotation stack if the stack layout collects its own guides first.
free_spaces
By default, ggheatmap() will align all elements of the
plot, which can sometimes lead to unwanted spacing. Consider the
following example:
ggheatmap(small_mat) +
scale_fill_viridis_c() +
anno_top(size = unit(30, "mm")) +
align_dendro() +
scale_y_continuous(
expand = expansion(),
labels = ~ paste("very very long labels", .x)
) +
anno_left(unit(20, "mm")) +
align_dendro()
#> → heatmap built with `geom_tile()`
In this case, the left annotation stack is positioned far from the
heatmap body due to the wide axis labels in the top annotation stack.
This occurs because the top annotation stack is aligned with the heatmap
body. To fix this, you can remove the left borders around the panel of
the top annotation stack by setting free_spaces = "l".
ggheatmap(small_mat) +
scale_fill_viridis_c() +
anno_top(size = unit(30, "mm")) -
plot_align(free_spaces = "l") +
align_dendro() +
scale_y_continuous(
expand = expansion(),
labels = ~ paste("very long labels", .x)
) +
anno_left(unit(20, "mm")) +
align_dendro()
#> → heatmap built with `geom_tile()`
One useful way to utilize free_spaces is to position the
guide legends next to the annotations. (Note the guide legend from the
bottom annotation):
heatmap_collect_all_guides +
# we only collect guides in the top and bottom side
quad_active() -
plot_align(guides = "tb") +
# 1. in the bottom annotation stack layout, we collect the legends in the
# left side
# 2. we remove the spaces of the left border in the annotation
anno_bottom() -
plot_align(guides = "l", free_spaces = "l")
#> → heatmap built with `geom_tile()`
In ggheatmap()/quad_layout(), the behavior
of the free_spaces and free_labs arguments
differs from guides arguments in plot_align()
when inheriting from the parent layout: - For top and
bottom annotations, it inherits from the left (“l”) and
right (“r”) axes. - For left and right
annotations, it inherits from the top (“t”) and bottom (“b”) axes.
free_labs
By default, we won’t align the axis titles.
ggheatmap(small_mat) +
scale_fill_viridis_c() +
ylab("Heatmap title") +
anno_top(size = unit(30, "mm")) +
align_dendro() +
ylab("Annotation title")
#> → heatmap built with `geom_tile()`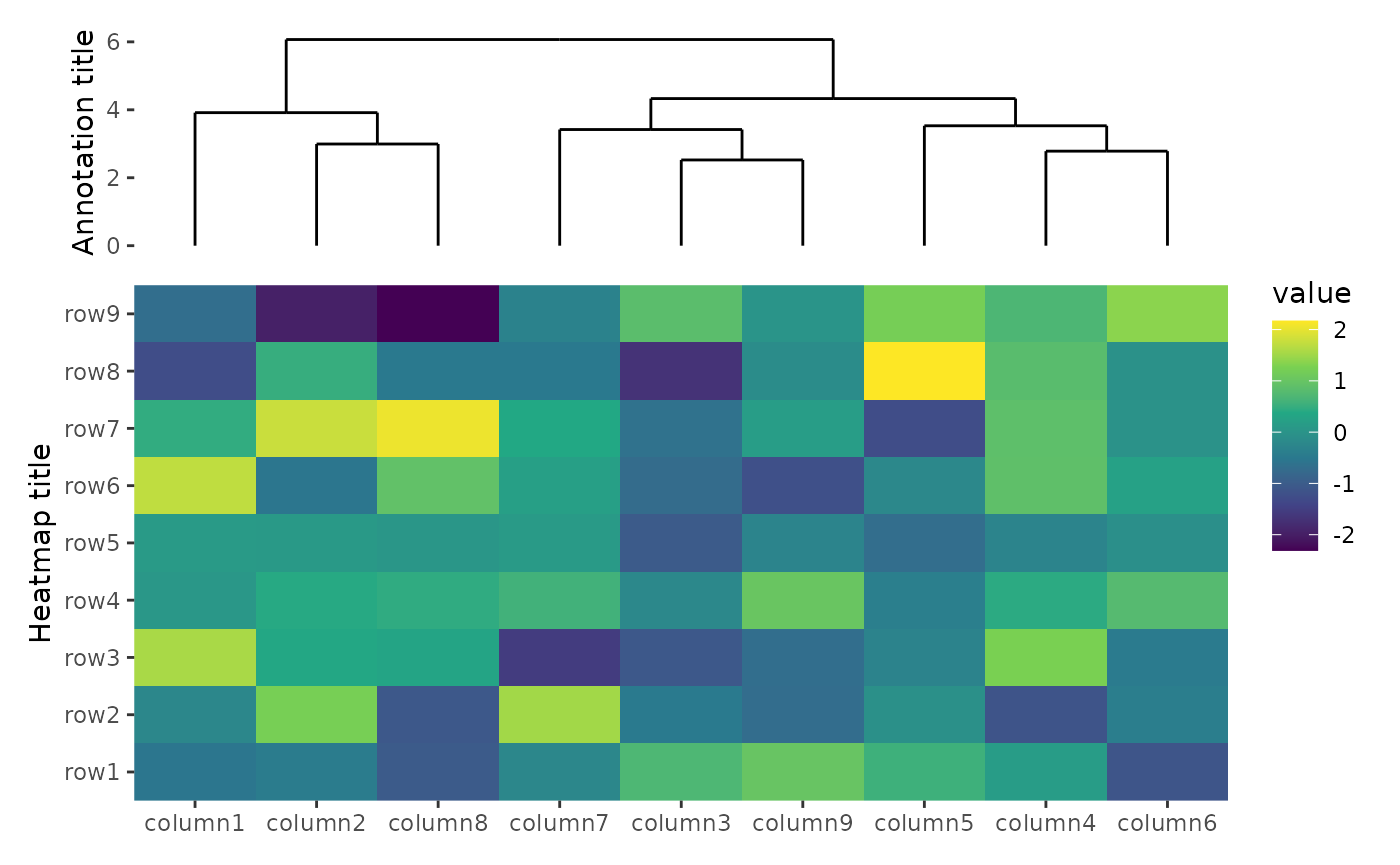
To align axis titles, you can set free_labs = NULL.
Alternatively, A single string containing one or more of axis positions
(“t”, “l”, “b”, “r”) to indicate which axis titles should be free from
alignment.
ggheatmap(small_mat) -
plot_align(free_labs = NULL) +
scale_fill_viridis_c() +
ylab("Heatmap title") +
anno_top(size = unit(30, "mm")) +
align_dendro() +
ylab("Annotation title")
#> → heatmap built with `geom_tile()`
Session information
sessionInfo()
#> R version 4.4.2 (2024-10-31)
#> Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
#> Running under: Ubuntu 22.04.5 LTS
#>
#> Matrix products: default
#> BLAS: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/openblas-pthread/libblas.so.3
#> LAPACK: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/openblas-pthread/libopenblasp-r0.3.20.so; LAPACK version 3.10.0
#>
#> locale:
#> [1] LC_CTYPE=C.UTF-8 LC_NUMERIC=C LC_TIME=C.UTF-8
#> [4] LC_COLLATE=C.UTF-8 LC_MONETARY=C.UTF-8 LC_MESSAGES=C.UTF-8
#> [7] LC_PAPER=C.UTF-8 LC_NAME=C LC_ADDRESS=C
#> [10] LC_TELEPHONE=C LC_MEASUREMENT=C.UTF-8 LC_IDENTIFICATION=C
#>
#> time zone: UTC
#> tzcode source: system (glibc)
#>
#> attached base packages:
#> [1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
#>
#> other attached packages:
#> [1] ggalign_0.0.5 ggplot2_3.5.1
#>
#> loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
#> [1] gtable_0.3.6 jsonlite_1.8.9 dplyr_1.1.4 compiler_4.4.2
#> [5] tidyselect_1.2.1 jquerylib_0.1.4 systemfonts_1.1.0 scales_1.3.0
#> [9] textshaping_0.4.0 yaml_2.3.10 fastmap_1.2.0 R6_2.5.1
#> [13] labeling_0.4.3 generics_0.1.3 knitr_1.49 tibble_3.2.1
#> [17] desc_1.4.3 munsell_0.5.1 RColorBrewer_1.1-3 bslib_0.8.0
#> [21] pillar_1.9.0 rlang_1.1.4 utf8_1.2.4 cachem_1.1.0
#> [25] xfun_0.49 fs_1.6.5 sass_0.4.9 viridisLite_0.4.2
#> [29] cli_3.6.3 pkgdown_2.1.1 withr_3.0.2 magrittr_2.0.3
#> [33] digest_0.6.37 grid_4.4.2 lifecycle_1.0.4 vctrs_0.6.5
#> [37] evaluate_1.0.1 glue_1.8.0 farver_2.1.2 ragg_1.3.3
#> [41] fansi_1.0.6 colorspace_2.1-1 rmarkdown_2.29 tools_4.4.2
#> [45] pkgconfig_2.0.3 htmltools_0.5.8.1